Are Government Subsidies Free Money? Understand the Truth
Types of Government Grants: Matching, Lump-Sum, and Functional
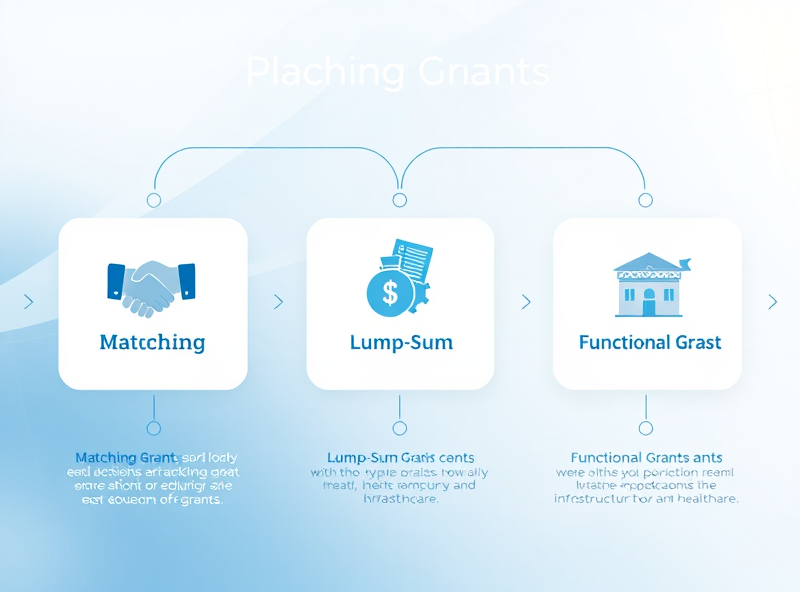
Government grants are often seen as ‘free money,’ but understanding their structure is essential to using them effectively. There are several types of government grants, each with its own purpose, eligibility criteria, and financial implications. Let’s break down the three most common types: matching, lump-sum, and functional grants.
1. Matching Grants: These require the recipient (often a state or local government, nonprofit, or business) to contribute a certain amount of funds to receive the grant. For example, if a federal agency offers a $100,000 grant with a 50% match requirement, the recipient must provide $50,000. Matching grants are designed to encourage shared investment and ensure commitment from the grantee. They are commonly used in infrastructure, education, and research projects.
2. Lump-Sum Grants: Also known as block grants, these are fixed amounts of money given for broad purposes. The recipient has more flexibility in how the funds are used, though they must still meet general guidelines. These grants are often used in areas like community development, health services, and social programs. Their flexibility makes them appealing, but they also require strong accountability and reporting mechanisms.
3. Functional Grants: These are allocated for specific functions or projects, such as building a school, launching a public health campaign, or upgrading public transportation. The funding is tied directly to the performance or delivery of a particular service. These grants often come with strict compliance requirements and are monitored closely to ensure objectives are met.
Understanding the type of grant you’re applying for can help you plan better, meet requirements, and maximize the impact of the funding. Whether you’re a nonprofit leader, small business owner, or local government official, knowing how these grants work can help you make informed financial decisions.
For more detailed information, you can visit the official U.S. government grants portal: https://www.grants.gov/
Must You Repay Subsidies? Tax and Accounting Insights

Government subsidies often sound like ‘free money,’ but the reality is a bit more nuanced—especially when it comes to taxes and accounting. While most subsidies do not require direct repayment like loans, they are not entirely without strings attached.
From a tax perspective, many subsidies are considered taxable income unless specifically exempted by law. For example, certain COVID-19 relief grants were taxable in some jurisdictions. This means that while you don’t repay the subsidy in cash, you may owe taxes on it, which can impact your net benefit. Always check with a tax professional or consult official tax guidance to understand how a specific subsidy affects your tax liability.
In accounting, subsidies must be recorded properly to ensure compliance and transparency. Depending on the type of subsidy—whether it’s a capital grant, operational support, or a tax credit—your accounting treatment will vary. For businesses, misreporting subsidies can lead to audits or penalties, so it’s crucial to document everything clearly and follow relevant accounting standards such as IFRS or GAAP.
Understanding these aspects can help you make informed decisions and avoid unexpected tax bills or compliance issues. If you’re unsure, the IRS provides detailed guidance on taxable and non-taxable government payments here: https://www.irs.gov/newsroom/taxability-of-government-grants-and-relief-payments
Real-World Support Programs for Businesses and Employment

Government subsidies often seem like ‘free money,’ but in reality, they are strategic tools designed to support economic growth, job creation, and innovation. These programs are funded by taxpayers and are carefully structured to achieve specific policy goals. For businesses and individuals, understanding how to access and use these subsidies can lead to significant opportunities.
One of the most impactful areas of government support is in business development and employment. For example, many countries offer wage subsidies to encourage companies to hire unemployed or underrepresented individuals. These programs reduce the financial risk for employers while helping people re-enter the workforce. In the U.S., the Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC) is a good example, offering tax incentives to employers who hire individuals from certain target groups.
Another form of support is grants for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These grants can help cover startup costs, research and development, or digital transformation efforts. For instance, the European Union’s Horizon Europe program provides funding for innovative startups and research institutions working on cutting-edge technologies.
In addition, training and upskilling programs are often subsidized to improve workforce readiness. Governments partner with educational institutions and private companies to offer subsidized courses in high-demand fields like IT, healthcare, and green energy. These programs not only help individuals gain valuable skills but also address labor shortages in key industries.
It’s important to note that while these programs are beneficial, they often come with eligibility requirements and application processes. Businesses and individuals should carefully review the criteria and prepare strong proposals or applications. Resources like government websites or local business development centers can provide guidance.
For more information on U.S. business support programs, you can visit the official SBA (Small Business Administration) website: https://www.sba.gov/funding-programs
Before You Apply: Key Conditions and Usage Compliance

Government subsidies can be a valuable financial support tool for individuals, businesses, and organizations. However, it’s important to understand that these funds are not simply ‘free money.’ Before applying, you must carefully review the eligibility criteria, usage restrictions, and compliance requirements associated with each subsidy program.
First, most government grants and subsidies come with specific conditions. These may include being part of a certain industry, operating within a particular region, or using the funds for designated purposes such as R&D, job creation, or sustainability improvements. Failing to meet these conditions can result in disqualification or even the obligation to repay the funds.
Second, usage compliance is critical. Once you receive a subsidy, you are typically required to report how the funds are used, often with documentation and periodic audits. Misuse or misreporting can lead to penalties, legal consequences, or exclusion from future funding opportunities.
Finally, always verify the credibility of the program through official government portals or trusted institutions. For example, in the U.S., grants.gov is a reliable source for federal funding opportunities.
Taking the time to understand these requirements not only protects you legally but also increases your chances of successfully securing and maintaining government support.
For more information on U.S. federal grants, visit: https://www.grants.gov/